Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent

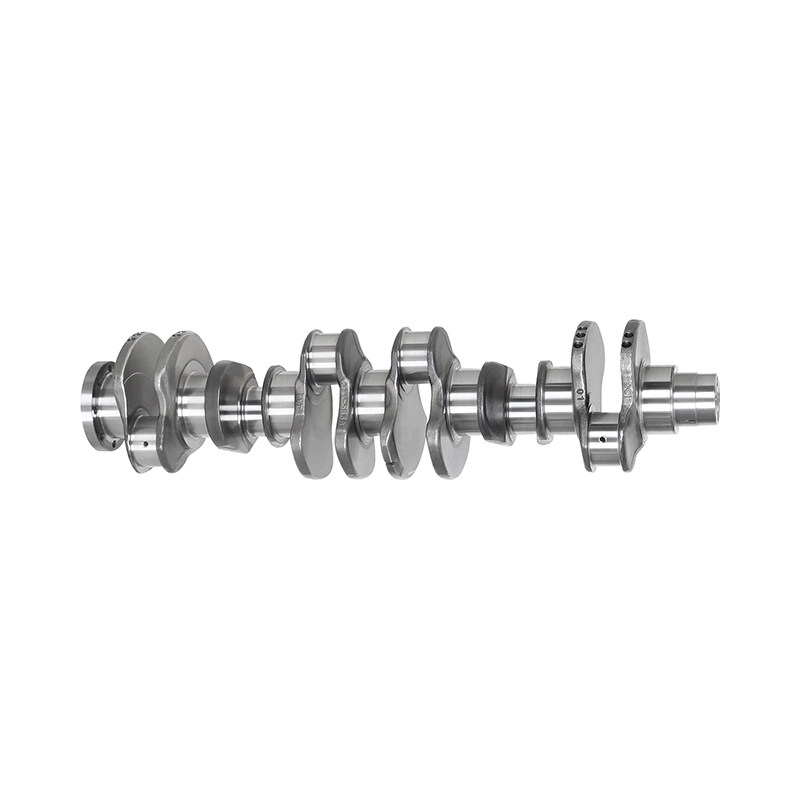
4D95 4D95L Engine/EGS45 EGS65 Diesel Generators Diesel Engine Camshaft
A diesel engine camshaft is a crucial component that plays a central role in controlling the opening and closing of the engine's intake and exhaust valves. It is responsible for managing the timing and duration of these valve events, which are essential for proper air intake, fuel injection, and exhaust gas expulsion
Function:
- The camshaft is responsible for converting the rotary motion of the engine's crankshaft into linear motion to open and close the engine's valves.
- It has carefully engineered lobes or cams that determine the valve lift, duration, and timing, which affects engine performance, efficiency, and emissions.
Timing:
- The camshaft is precisely timed with the engine's crankshaft to ensure that the intake and exhaust valves open and close at the correct moments in the engine's four-stroke cycle (intake, compression, power, and exhaust).
Types:
- Camshafts come in various designs, such as overhead camshaft (OHC) and overhead valve (OHV) configurations, depending on the engine's design and purpose.
Construction:
- Camshafts are typically made from high-strength materials, such as hardened steel or alloy, to withstand the mechanical forces and heat generated during engine operation.
Drive Mechanism:
- The camshaft is driven by a timing belt, timing chain, or gears, which are connected to the crankshaft. This drive mechanism ensures that the camshaft rotates at half the speed of the crankshaft.
Valvetrain Components:
- The camshaft interacts with valvetrain components, including lifters, pushrods, rocker arms, or directly with the valve stems, to transmit motion and control the valves' actions.
Keep Engine with Long-term Stable Operation:
The high-precision machining and optimized design of the camshaft can improve the stability and reliability of the engine, reducing the risk of malfunctions and repairs and ensuring long-term stable operation of the engine. The camshaft is manufactured with high-precision machining techniques, ensuring that it meets international standards and provides reliable engine performance. The optimized design of the camshaft improves the engine’s stability and reliability, reducing the risk of malfunctions and repairs. This feature ensures that the engine can operate smoothly and reliably over the long term, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. With its focus on high-precision machining and optimized design, the camshaft is an excellent choice for those seeking a reliable and durable engine component that can withstand the rigors of heavy use while also providing excellent performance and stability.
The Special Design through Serious Quality Test Maintains Its Normal Operation:
The design and manufacturing process of the camshaft undergoes strict quality control to ensure that it can withstand the high-speed operating environment and ensure the normal operation of the engine. The camshaft is designed and manufactured with high-quality materials and advanced manufacturing techniques, ensuring that it meets international standards and provides reliable engine performance. The camshaft undergoes rigorous quality control during the manufacturing process, ensuring that it can withstand the high-speed operating environment and provide stable and reliable engine performance. This feature ensures that the engine can operate smoothly and reliably over the long term, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Before sending, they will be also tested, ensuring its normal usage, and it does not make any trouble for you.
Product Parameter:
|
Product Name |
Engine Camshaft |
|
Application |
Engineering Machinery Engine |
|
OEM Number |
6205-41-1300 |
|
Car Number |
Komatsu |
|
Size |
STD |
|
Engine Number |
4D95 / 4D95L / EGS45 / EGS65 |
|
Condition |
100% Brand-new |
|
Warranty |
6 Months |
|
Packing |
Neutral Packing |
|
Application |
Machinery Repair Shops, Construction Works, Energy & Mining |
What is A Camshaft?
The camshaft is located on top of the engine. It is an essential component of the engine valve mechanism, allowing air and fuel to come into the combustion chamber and allow gases to escape after combustion.
The latest internal combustion engines can have up to four camshafts (or two camshafts). Each cylinder has four valves (two intake and two exhaust ports). Only a single camshaft setup is configured on each valve.
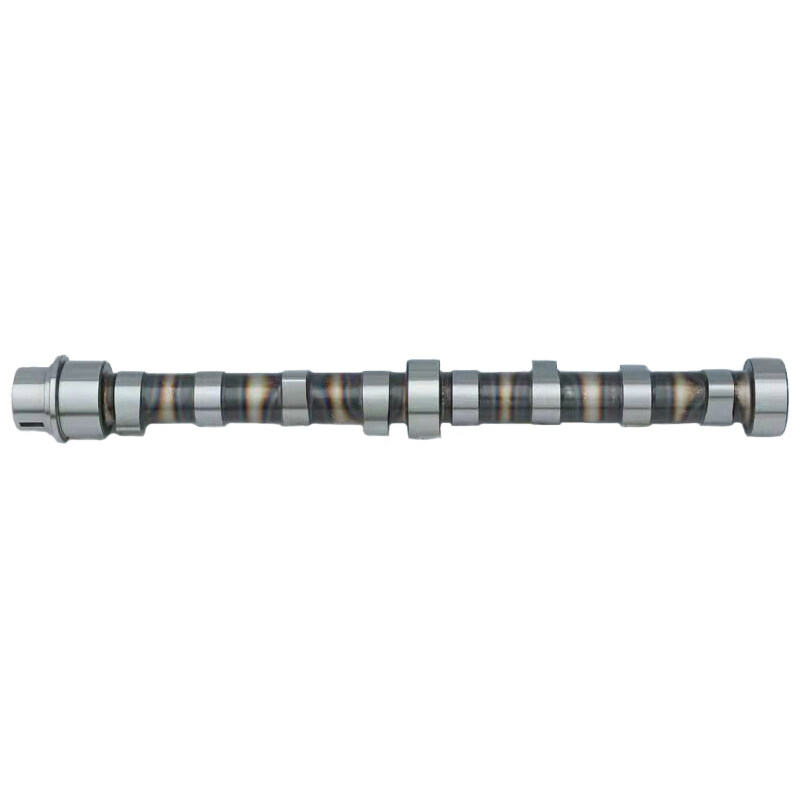

How does Camshaft work?
The main objective of the camshaft is to open the suction valve and exhaust valve at the appropriate time. The crankshaft drives to this shaft. It is linked with the crankshaft through a belt or meshing gears.
The movement of the camshaft is slower than the crankshaft. It completes one revolution after two revolutions of the crankshaft. In a four-stroke engine, a camshaft works in the following way:
1.As the piston moves from TDC to BDC (downward), it transfers its motion to the crankshaft.
2.The crank receives piston motion and transforms this motion into rotary motion, and starts rotating.
3.The crankshaft is connected with the camshaft through gear or belt.
4.As the crankshaft transfers its rotary motion to the camshaft, the camshaft converts this rotary motion into reciprocating motion and presses the inlet valve and opens it.
5.As the valve opens, the fuel starts to enter the combustion chamber.
6.After suction and compression strokes, the combusted air-fuel mixture expands in the chamber, which forces the piston to move downward.
7.During the downward motion of the piston, again, the crankshaft receives motion and moves the camshaft.
8.As the cam of the exhaust valve receives this motion, it presses the exhaust valve and opens it, which allows exhaust gases to move out of the combustion chamber.
Camshaft Construction Material
The solid material is most commonly used for the manufacturing of the camshaft. This is because such camshafts provide great rigidity. Cast iron is also used for the manufacturing of camshafts because cast iron delivers more strength.
The camshafts made of the chilled iron process can provide excellent wear resistance because the chilling method hardens the material. Different materials mix with iron to generate the most appropriate features for their applications.
Some industries also utilize billets when less production and excellent quality are needed. But this process demands high time and cost compared to other processes. These shafts manufacture through machining, casting or forging on milling and lathe machines. They are manufactured by forging, casting and machined on lathes and milling machines.
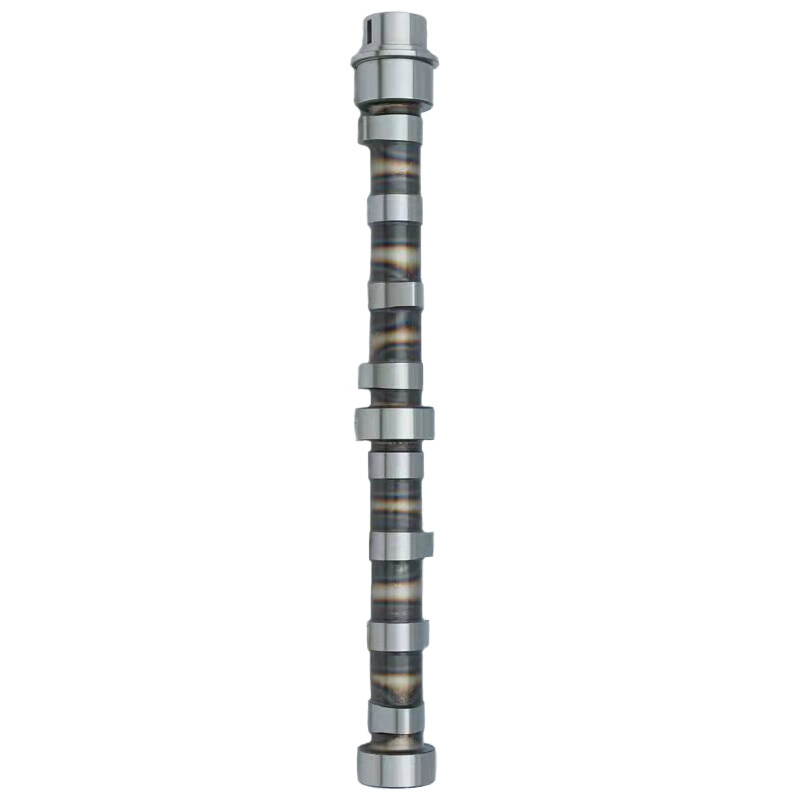

Reasons for a Camshaft failure
There are multiple reasons for the camshaft failure. The most reasons for the failure of the camshaft are given below:
1.Due to the wrong pressure of the valve spring.
2.Because of lobe wear.
3.Insufficient brake-in.
4.Due to the damaging of the cam.
5.Due to the large axial play of the camshaft.
6.Use of oil filter with the new cam.
7.Due to mechanical interference such as seal interference, spring coil bind, valve and piston interference, rocker arm grooves, and screw interference.
8.Low-quality use of camshaft material.